Have you ever wished to know what happens when there is transportation of goods without documents? Most businesses, and more so the small ones, often experience delays, incur penalties, or get confused when transporting because they are unaware of one important thing: the eWay bill. An eWay bill is one of the documents to be carried when transporting goods (and the gross amount exceeds 50,000 rupees). It belongs to the GST system and allows the government to monitor the items that are transported in the country.
Are you starting a business or new to this? No problem. We will all clarify everything in simple terms here in this blog: what an eWay bill is, who should get it, when it should be procured, and how to create one step by step.
What is eWay Bill?
The eWay Bill is a vital web-based document needed in the movement of goods that are part of GST (Goods and Services Tax) in India. According to the provisions of GST, every registered person is required to issue an e-way bill before moving goods of greater than 50,000, whether on the basis of a single invoice, invoice, or delivery challan. Such a bill has to be prepared via the official gateway access point ewaybillgst.gov.in. The main aim is to make it transparent, minimise tax evasion, and ensure compliance when goods are being moved across borders both locally and nationally.
After the generation of the eWay Bill, a separate and specific E-Way Bill Number (EBN) takes place and is issued to the supplier, the recipient, and the transporter so that all three parties are in a position to trace the movement of the shipment in real time. Besides the web portal, users may access the eWay Bill generation, update or cancellation by using SMS, mobile application, or system-to-system integration via APIs, an option that is chiefly utilised by large businesses.
It is also worth noting that to avoid penalties and remain accurate, the GSTIN (GST Identification Number) of the parties involved should be checked by the parties with the GST search tool before generating the bill. The eWay Bill system, in general, allows simplifying logistics activities and legal compliance concerning the GST.
Who has to generate the eWay Bill?
Now that we know what is eWay Bill, let’s look at who is responsible for generating it:
- A seller should also generate it in case he or she is delivering goods valued at more than 50,000 (INR).
- If the buyer is accepting the goods of an unregistered seller, then the buyer is required to produce the bill.
- In case an individual is transporting goods on behalf of another person, and no one has rendered the bill, it should be generated by the transporter.
- You have to generate an eWay Bill in case you are simply transporting finished goods to repair, returns or job work.
For example, imagine you run a store and are sending ₹70,000 worth of furniture to another city — you need to make an eWay Bill before shipping the furniture.
Cases when eWay Bill is Required?
Some of the common situations where you need an eway bill include:
- When goods worth more than ₹50,000 are moved
- If you’re sending goods across state borders (even if the value is below ₹50,000 in some cases)
- When moving goods within your own state in certain regions
- When moving goods for reasons other than sale – like samples, repairs, exhibitions
Even if not compulsory, businesses can choose to generate eWay Bills voluntarily for better record-keeping. Knowing about eWay Bill and situations when it’s required can help you avoid penalties and delays in transportation.
Cases When You Don’t Need an eWay Bill
Let’s also explore the situations where eWay Bills are not needed:
- The mode of transport is Non-Motor Vehicle
- Goods transported from Customs port, Airport, Air cargo complex or Land Customs Station to Inland Container Depot (ICD) or Container Freight Station (CFS) for clearance by Customs
- Goods transported under Customs supervision or under Customs Seal
- Goods transported under Customs Bond from ICD to Customs port or from one Custom Station to another
- Transit cargo transported to or from Nepal or Bhutan
- Goods meant for personal consumption
- Transporting Precious or semi precious stones
- LPG supply to household etc
So, while knowing cases where the eWay Bill is important, it’s equally useful to know when you don’t need one.
Documents Required to Generate an eWay Bill
To generate the eWay Bill, here’s what you’ll need:
- A valid Invoice or Bill of Supply
- GSTIN (if you’re registered under GST)
- Transport details – vehicle number or transporter ID
- Product details – name, quantity, price, HSN code
- Shipping address of the buyer or recipient
All of this information is entered into the eWay Bill portal to create the bill, which gets a unique 12-digit number.
What Does an eWay Bill Look Like?
An eWay Bill has two main parts – Part one and Part two, in which each part plays a specific role in ensuring a smooth and transparent transportation process under GST.
- Part one of the eWay Bill contains the important details related to the goods and the transaction. These details are generally provided by the supplier or the registered person initiating the movement of goods. This includes details such as:
- Invoice or challan number
- Date of supply
- GSTIN of the recipient
- Pincode of delivery
- Value of the goods
- HSN code ( If your turnover is up to ₹5 crore, using HSN codes is compulsory for B2B invoices (with at least 4-digit codes) but optional for B2C. For turnovers above ₹5 crore, HSN codes are mandatory for both B2B and B2C invoices, and you must use a minimum of 6 digits.)
- Reason for transportation (selected from predefined options)
- Transport document numbers like goods receipt number, railway receipt, etc.
- Part two includes transportation details, such as:
- Vehicle number (for road transport)
- Transporter ID (for all modes)
- Transport document number and date (especially for rail, air, or ship)
After completing and submitting the eWay Bill online through the eWay Portal, a 12-digit eWay Bill Number (EBN) is registered. This number is consignment-specific and it is available to the supplier, recipient and the transporter. An eWay Bill is also provided in the form of a printable one and can include a QR code.
It is possible to verify and scan this QR code during inspections. This is a requirement that a physical or electronic copy of this bill must accompany the person delivering the goods in transit.
The bill may also be produced, updated(Part 2 can only be updated), or cancelled/ extended not only using the portal but also using SMS or a mobile application or even integration through an API application, which is helpful in case of large amounts of shipments daily managed by businesses. It is better to check the GSTIN of any party in the bill beforehand through the GST search tool, as it maintains accuracy and prevents compliance problems. With this format and the process, companies can legally transport their products, thereby ensure smooth transit and avoid penalties under GST
How to Generate an eWay Bill
The easiest way to make an eWay Bill is through the official GST eWay Bill portal. Steps on how to do it:
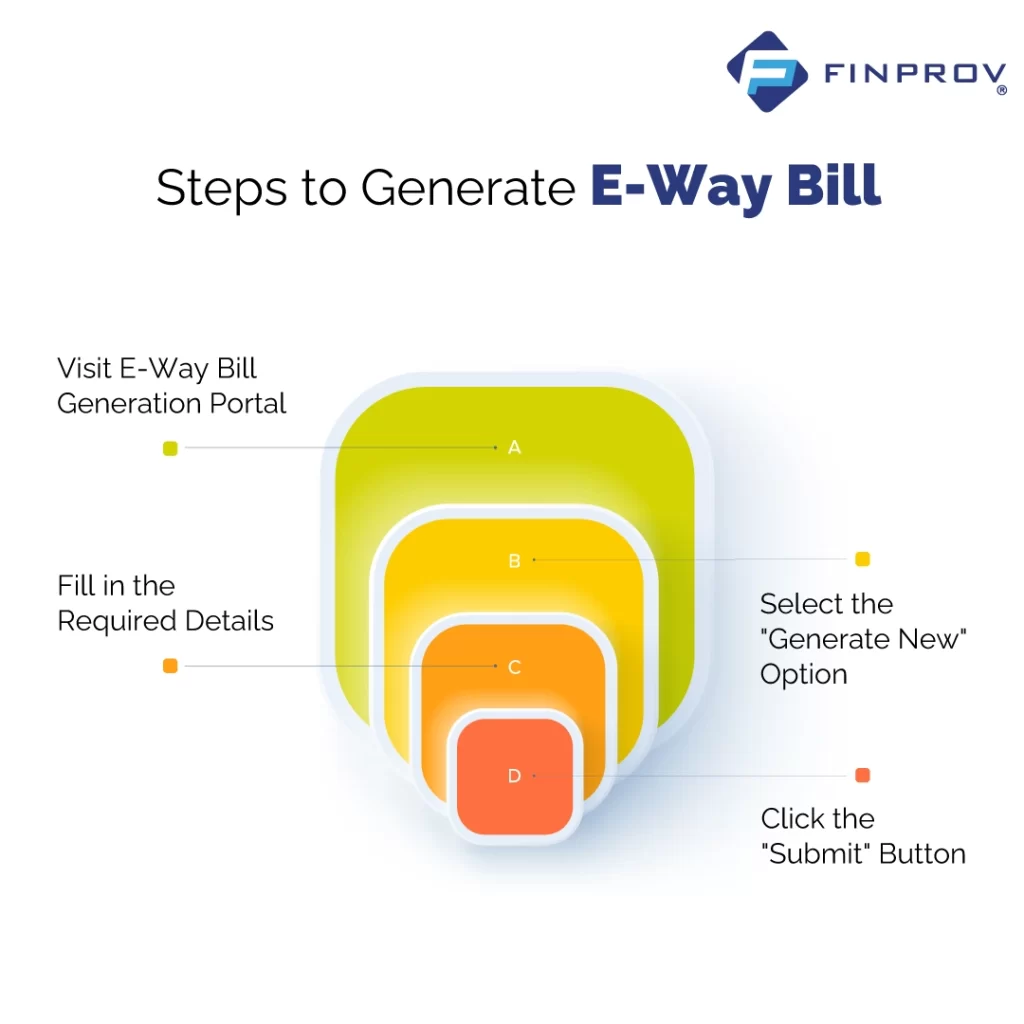
- Visit ewaybillgst.gov.in
- Log in using your GST username and password
- Click on the “Generate New” option
- Fill in Part A with the invoice and product details
- Fill in Part B with transport details
- Click Submit – you’ll get the eWay Bill with a number and QR code
- Print it or save it on your phone to show during transport
There are other ways too:
- Through SMS, if you don’t have internet
- Using a mobile app
- Through software integration (API) for businesses with large orders
If you’ve understood what an eWay Bill is, generating one becomes a routine task in business.
Validity of an eWay Bill
The eWay Bill doesn’t last forever. Its validity depends on distance:
- Up to 200 km -valid for 1 day
- For every extra 200 km or part, add 1 more day
For example:
If your goods are travelling 300 km, then it is valid for 2 days. For large or heavy goods (called ODC- Over Dimensional Cargo), the rules are different: 1 day for every 20 km. If needed, you can also extend the validity- but you must do it before the bill expires.
What Happens If You Don’t Generate One?
If you don’t generate an eWay Bill when it’s required, the consequences can be serious:
- Goods can be stopped and detained
- You may face a penalty of ₹10,000 or the tax amount, whichever is higher
- It may affect your GST compliance rating
- Your business reputation may suffer with customers or transporters
So knowing what is eWay bill under GST, how to generate it, and staying compliant is very important for smooth operations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the eWay bill is vital for the legal transport of goods under GST, especially for consignments exceeding ₹50,000. It helps prevent delays, penalties, and unauthorised movement. The key components include the invoice details, transporter ID/vehicle number, and the GSTINs of the supplier and recipient. The bill can be generated, updated, or cancelled via the portal, SMS, mobile app, or API—making it convenient for businesses with frequent shipments. Always verify GSTINs to ensure compliance. For more help, visit the official eWay Bill portal or consult a tax professional.
If you want to enhance your understanding of the e-way bill and its diverse aspects, we recommend enrolling in our comprehensive e-way bill course. Finprov, an ed-tech institute, offers a comprehensive course on e-way bill and other accounting courses. The e-way bill course covers various topics such as the e-way bill format, how to generate an e-way bill on the e-way bill portal, who should generate e-way bill, e-way bill rules, validity and much more. Enrolling in this course, you can better understand the e-way bill and its business implications.
At Finprov, a hands-on approach is key to effective learning. Our courses are designed to give students real-life situations and projects to equip them with practical knowledge that will enable them to perform effectively in the job market. Students are taught by our competent instructors through a solid theoretical base. In contrast, practical applications are highlighted to ensure the students can practice their newly gained skills in the workplace.
FAQs
Q1. What is an eWay Bill?
An eWay Bill is a document that must be filed when the value of goods is more than 50000 rupees. Before goods are transferred, it has to be created on the GST eWay Bill portal. It makes GST compliance and tracking of shipments.
Q2. Why is the eWay Bill required?
According to the GST law, it is a requirement that one carries an eWay Bill when transporting goods worth more than 50,000. It serves as evidence that goods are transported legally and with due tax documents.
Q3. Is the eWay Bill needed for all goods?
The majority of the goods demand an eWay Bill when being transported. But then, there are some exceptions, such as some handicrafts or job-work goods, even though they may be less than 50,000 rupees. The complete list of exemptions to the official rules can be viewed.
Q4. Who can generate the eWay Bill?
It can include the supplier or recipient (if registered under GST), a transporter (registered or unregistered with transporter ID), an unregistered person moving goods can also generate the eWay Bill for their use, and even a third party or an e-commerce operator can generate it under specific cases.
Q5. What are the prerequisites for generating an eWay Bill?
To generate an eWay Bill, the person must be registered under GST and have login credentials, registered or enrolled on the eWay Bill portal, must have a valid invoice or bill, should have details of the vehicle number or transporter ID and now the delivery location, product details, and value.