When crafting financial statements, businesses follow a systematic process known as the accounting cycle. This systematic approach involves some steps to transform fundamental financial data into comprehensive, accurate reports. The accounting cycle simplified financial reporting, providing business owners with a structured and straightforward way to manage their financial information. Let’s read the steps in the accounting cycle, review its primary steps, and explore how advanced accounting software can automate and streamline this intricate process.
What Do You Mean by Accounting Cycle?
The steps in the accounting cycle are designed to simplify financial responsibilities for business owners, accountants, and bookkeepers. Comprising eight essential steps, this cycle aids in identifying, analyzing, and recording financial information, offering a clear guideline for accurate bookkeeping tasks.
This process records a business’s transactions from initiation to conclusion, enhancing organizational efficiency. It encompasses accounts, including T-accounts, credits, debits, journal entries, financial statements, and book closings.
One primary goal of the critical steps in the accounting cycle is to ensure the accurate recording and reflection of a business’s finances during the accounting period, functioning as a comprehensive checklist at the period’s conclusion. Companies can execute the monthly, quarterly, or annual accounting cycle, aligning with the frequency needed for financial reporting.
Essential Steps in the Accounting Cycle
Here’s a detailed overview of the steps in the accounting cycle. After completing all the steps, businesses can seamlessly transition to the next accounting period.
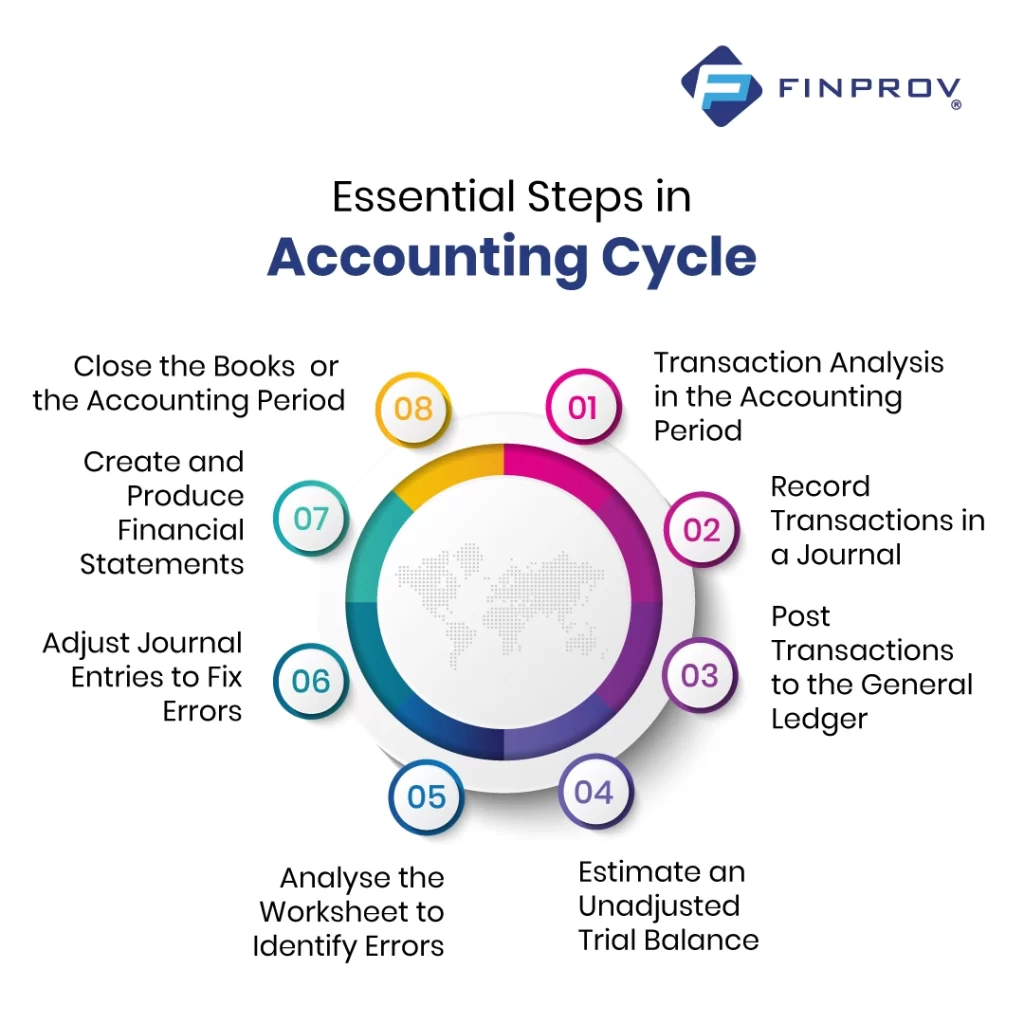
Finding out and Researching Transactions During the Accounting Period
The accounting cycle commences with identifying and collecting information about transactions throughout the accounting period. It involves analyzing the impact of each transaction, covering aspects such as expenses, asset acquisition, borrowing, debt payments, debts acquired, and sales revenues.
Record Transactions in a Journal
After identifying and analyzing transactions, the next step involves recording them as journal entries in your accounting software or ledger. While some businesses use point-of-sale technology to combine these steps, it’s still vital to track expenses carefully. The timing of identifying expenses and income depends on your chosen accounting type and method. Accrual accounting recognizes transactions when incurred, while cash accounting considers transactions when cash changes hands.
Post Transactions to the General Ledger
After recording transactions in journals, they are subsequently posted to the general ledger, a pivotal component in accounting that serves as a master record for all financial activities. The general ledger categorizes financial activities across different accounts, providing a comprehensive view of the company’s finances. Notably, the cash account within the general ledger holds significant importance as it reflects the available cash at any given time.
Estimate an Unadjusted Trial Balance
Following the steps within the accounting period, the unadjusted trial balance is calculated after the period concludes, and all transactions are identified, recorded, and posted. This trial balance provides insights into the unadjusted balances of each account, which are then carried forward for further testing and analysis.
The unadjusted trial balance plays a critical role in ensuring the accuracy of financial records by confirming that total debits match total credits. Any discrepancies indicate missing or misaligned elements. This step is instrumental in uncovering anomalies, such as payments assumed to be collected or invoices presumed to be cleared but still outstanding.
Analyze the Worksheet to Identify Errors
Analyzing worksheets in this step of the accounting cycle becomes crucial to identifying entries requiring adjustments. As every transaction is registered as a credit or debit, this step ensures the equality of the total credit balance and debit balance. It is particularly essential for matching revenue and expenses in accrual accounting. Beyond error identification, this step sets the stage for making adjustments in the subsequent phase.
Adjust Journal Entries to Fix Errors
As the accounting period concludes, adjustments to journal entries are made to rectify any errors or anomalies identified during the worksheet analysis. As the final step before generating financial statements, this phase demands a meticulous review, supported by a new adjusted trial balance. This comprehensive check ensures the accuracy and integrity of the financial records.
Create and Produce Financial Statements
Following the adjustment of entries, this step involves the creation of essential financial statements. Most companies generate balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements. These statements provide a comprehensive overview of business events throughout the accounting cycle.
While balance sheets and income statements depict past events, cash flow statements project and track the business’s cash flow, offering valuable insights. Financial statements are crucial for comparisons with other companies and play a significant role in helping business owners interpret their finances and formulate growth strategies.
Close the Books for the Accounting Period
This is one of the steps in the accounting cycle to make closing entries and finalize expenses, revenues, and temporary accounts during the end of the accounting period. This involves closing temporary accounts (e.g., expenses and revenue) and transferring net income to permanent accounts like retained earnings.
With the books closed, the financial statements provide a comprehensive performance analysis. Subsequently, the accounting cycle restarts for the new reporting period, providing a suitable time for paperwork filing and planning for the upcoming accounting period.

Efficient business processes in accounting are essential for maintaining accurate financial records and ensuring the smooth operation of financial tasks within an organization. To explore the knowledge of accounting, consider enrolling in accounting courses online, where Finprov, a premier ed-tech institute, offers cutting-edge programs. Our comprehensive accounting training, featuring top-tier courses like CBAT, PGBAT, Income Tax, Practical Accounting Training, PGDIFA, DIA, GST, SAP FICO, Tally Prime, and MS Excel, is tailored to meet the various needs of learners at various career stages.
With a focus on hands-on practical training, our courses equip you with skills crucial for real-world application. At Finprov, we are committed to empowering graduates and professionals, going beyond educational offerings to ensure your success. Our job-oriented courses and placement assistance open doors to some of the highest-paying jobs in India, providing a pathway to elevate your skills for a more promising and prosperous future. Embark on your journey to success with Finprov, where education seamlessly aligns with opportunity.